The Goods sector had the highest number of jobs at 30 million in the 1980s. Even then it was lower than the services sector which was employing 69 million during the same period. Today the Services sector employs 110 million people. Four out of five Americans are employed in the services sector. The services sector accounts for around 80% of US GDP. Similarly export of Services trade has shown continuous increase from the 1980s and has always shown a positive balance. Regulations play a significant role in the trade in the services sector just as tariffs play a significant role in Goods trade. At present, when there is so much discussion going around tariffs, it is equally important to know about the regulations that have and will shape the services trade which has the prominent share in the economy. In this article, I discuss in brief about the growth of the services sector, the regulations and the impact of regulations in services trade and globalization.
From Goods to Services Economy
The services sector accounts for 80% of US GDP. Since the 1960s, the share of services has seen steady growth. The economy once dominated by agriculture was taken over by the manufacture of Goods. The Goods economy was taken over by services and it exceeded the Goods economy from the 1970s. The following chart1 shows the growth of trade from the services sector since the 1980s. The sector has shown consistent growth and has remained on the positive side, i.e. exports have always been greater than imports.
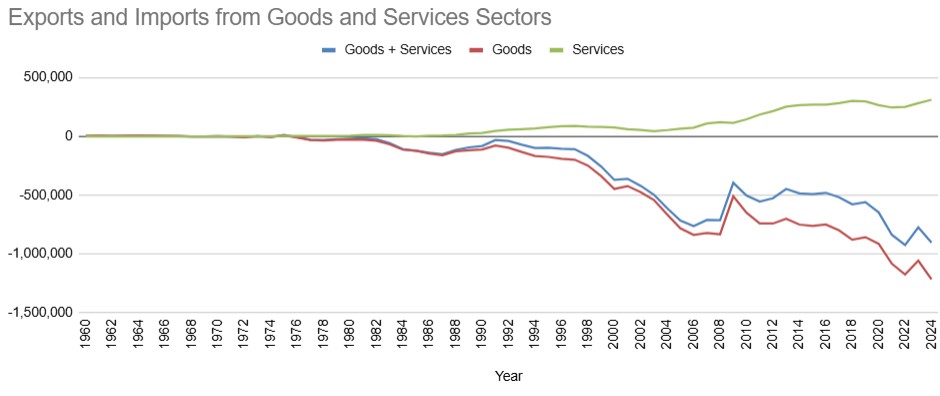
There were many factors which resulted in the growth of the services sector: (1) Baby boomer generation, born between 1945 and 1964, were highly educated (2) The highly educated workforce of late 1970s excelled as consultants and were able to add value-addition to Goods (3) US consumption increased and manufacturing in US alone was not enough to meet the demand at a price affordable for the huge consumer base (4) Manufacturing was shifted to countries which had less labor costs (5) China and countries in South East Asia started to emerge as a manufacturing powerhouse at lesser cost and higher productivity (6) The growth of Information Technology industry which aided in implementation and delivery of services (7) Deregulation in the 1980s resulted in increased competition in various service industries, leading to innovations and expanded job opportunities (8) The growth of franchises in the country which brought standardization, uniformity and predictability in quality and delivery of services.
The majority-Goods and majority-Services economies were complementing each other which allowed for gradual transition from goods to services economy2. At one end, the productivity increased resulting in production of more goods. When more goods are produced, there needs to be a market to be able to consume the goods produced. This arose the need to market the goods, add more value to the goods to make it attractive for the people to purchase the products, and it also required other services such as transportation to retail services to repair services and so on depending upon the product. Thus manufacturing and services complemented each other and manufacturing slowly gave rise to services as a major economic sector. Further, when there were opportunities to get the goods manufactured at a lower cost outside the country, the manufacture of goods started to happen outside the country and the add-on value-added services were happening in the USA resulting in shrinkage of goods economy and expansion of services economy.
Expansion of Services Sector
Several services blossomed to facilitate the adoption and usage of manufactured products by the market. The business and repair services, Finance services, Insurance services, Professional and business services, legal and auditing services and others filled the gap between producers and consumers. Transportation, Logistics and Retail services brought the products to the reach of consumers. Information technology services enabled writing software applications to conduct these businesses with ease and efficiency. Telecommunication services connected people across countries, opening up communications and expansion of services.
Apart from these services, services such as Healthcare and Education which were primarily for social growth and societal welfare witnessed huge growth. The manufacture of pharmaceuticals, drugs and medical devices were brought to the benefit of the society at large by building the infrastructure for healthcare services such as hospitals, clinics, Insurance providers, medical retail stores and so on. The Education sector started to offer many streams of programs to serve the needs of the growing services sector. The entertainment and leisure sector opened up recreational services such as televisions, travel, hospitality, restaurants and more.
The following chart1 shows the various services and their growth over the years from 1999 to 2024.
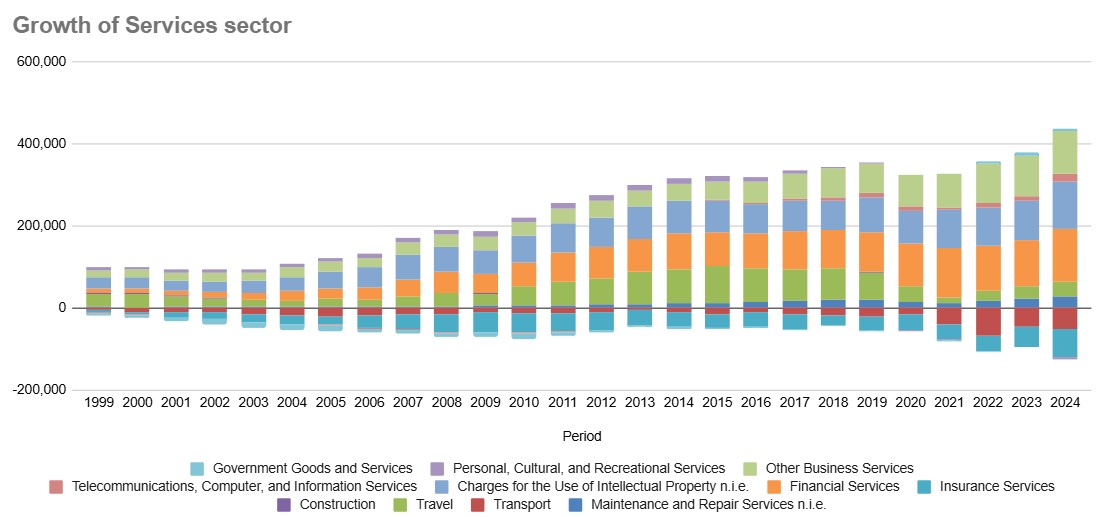
Each sector aided in the growth of the economy by bringing the products closer to customers and by doing so created millions of job opportunities. Now four out of five Americans are employed in the Services sector.
Innovation in Services Sector
Just as the Good sector needs science, technology and innovation, the Services sector needs innovation and the business acumen to bring the products to the customers. Understanding of the market, assessing the needs of the market, thinking of suitable applications, enriching user-experience all require business acumen and a broad understanding of the various facets of the market. The highly educated workforce from the baby boomer generation propelled the innovation and acumen needed for the expansion of the services sector.
If I were to talk about the software industry, until the late 2000s software which was primarily delivered as a product, witnessed a shift in the delivery model. Software started to be provided as a service and it is popularly called as ‘Software-As-A-Service’ (SaaS) model. (To go back, Software was itself a service which was provided over the hardware and then with this SaaS model, software by itself was provided as a service). With the development of Cloud infrastructure and stable internet systems, SaaS delivery models achieved higher reach for software products in the market and at the same time also provided more affordability for the customers.
During the course of innovation and delivery of services, considerable knowledge, ideas and data are generated as valuable resources. Keeping track of these resources and preserving them is of high priority in the services economy. For e.g. in the software industry, millions of lines of code is written for development of applications. Proper documentation of hierarchy of thoughts and comments in the code are absolutely essential to pass on the knowledge (knowledge transfer) and to continue providing the services.
Regulations in Services sector
The deregulation in the 1980s was partly responsible for expansion of the Services sector. It increased competition among service providers in the financial sector. Due to competition, they opened more branches to reach more customers and hired more employees. Easing of regulations pertaining to capital flows and money lending propelled fast spread of financial globalization. The subsequent financial crisis and scandals created the need to enforce strict regulations and rules for monitoring the finance, banking and insurance industries.
Regulations exist in all services sectors. Pharmaceutical and healthcare industries are highly regulated. So are the Airlines and Telecommunications industries. Equipping and staying updated with the appropriate sector-relevant regulatory frameworks is critical for proper and efficient conduct of businesses in the services sector. Similarly understanding regulations across countries is essential for international trade on services. In a world where services play a major role in economic growth, any change in regulations or barriers in services trade will result either in visible progress or setbacks.
Regulations can be set or enforced on several policy areas such as in restrictions on foreign entry, restrictions on movement of people, setting barriers to competition, setting rules for transparency and in other discriminatory measures such as in taxes, subsidies, procurements, national standards, etc..3 The document Services Trade Policies and the Global Economy published by OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) elaborates on the different parameters that would come under the regulatory framework for the above mentioned policy areas. Further the Services Trade Restrictiveness Index (STRI) available in the OECD online regulatory database gives an overview of services barriers of trade across countries and service sectors. The database can be accessed through the URL http://qdd.oecd.org/subject.aspx?Subject=STRI.
Conclusion
Several factors such as an educated workforce, higher productivity, higher consumerism, emergence of low-cost manufacturing centers outside the USA shifted the US economy from goods-based economy to services-based economy. 4 in 5 Americans today are employed in the Services sector. The growth of the Services economy fostered innovative thinking and business acumen to find suitable applications and market for the manufactured products. As the Services industry grew, several regulations were put in place to protect consumers and to make businesses accountable for their services. Equipping ourselves with the skills required to develop market awareness and business acumen (through education and/or experience) will boost the already growing services economy. Just as tariffs play protectionist roles in goods trade, regulations play a role in the services industry. Understanding those regulations for different sectors in services will help to hone the skills and requirements for the services economy.
Bibliography
1. U.S. International Trade in Goods and Services
2.https://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/1984/04/art2full.pdf
3.Services Trade Policies and the Global Economy by OECD







Leave a Reply